PHP First Script
|
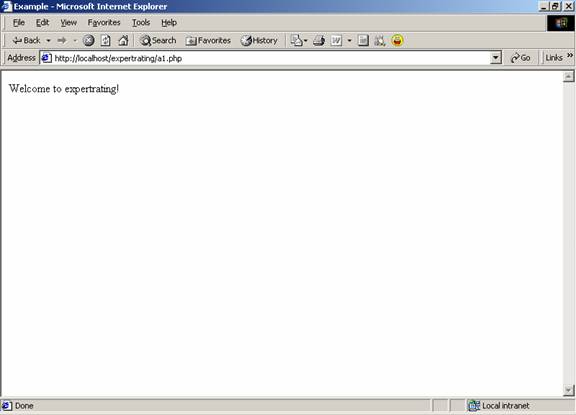
Now that you have installed all the support software for running PHP, you are ready to learn how to do a PHP script. Writing a PHP script is very simple. No special software is needed, except a text editor like Notepad in which the script is written. You have to run that code on your web browser and you are ready with your first PHP script. The First Script A PHP file normally contains HTML tags and some PHP scripting code. A PHP scripting block always starts with <?php and ends with ?>. A PHP scripting block can be placed anywhere in the document. In PHP scripting each line of code must end with a semicolon (;). The semicolon acts as a separator and is used to distinguish between two sets of instructions. There is a PHP script in the example given below. This script will display the words “Welcome to expertrating!” in the web browser. There are two basic statements to output text on the browser with PHP: echo and print. In the example given below, the echo statement is used to display text.
Output
|
||||||||||||||||
How to run your PHP script?
- Save that script in the web server’s root directory.
- Open your web browser and type “//localhost/directory name/filename.php” and then press enter.
- By doing this the script will run in your browser.
Variables
Different languages have different ways of defining a variable. Similarly, in PHP variables are defined in a unique manner. All variables in PHP start with a $ sign symbol. Variables may contain strings, numbers, or arrays.
If you want to assign a string to a variable, then you have to put that string into quotes “ “ like: “Hello! How are you?”. If you want to assign a number to a variable then there is no need to include it into the quotes.
The code to display a variable on the screen is same as the code to display normal text. The variables are also displayed with the echo command e.g. echo $abc.
This is an example in which a string is assigned to a variable, which is further displayed on the web browser.
| Example |
|
<html> |
|
<head> |
|
<title>Example</title> |
|
</head> |
|
<body> |
|
|
|
<?php |
|
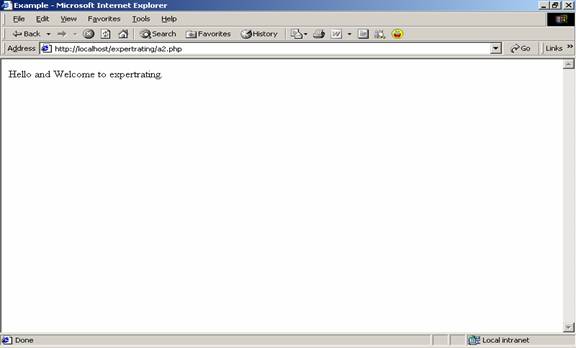
$txt ="Hello and Welcome to expertrating."; |
|
echo $txt; |
|
?> |
|
|
|
</body> |
|
</html> |
Output:
This is an example in which a number is assigned to a variable, which is further displayed on the web browser.
| Example |
|
<html> |
|
<head> |
|
<title>Example</title> |
|
</head> |
|
<body> |
|
|
|
<?php |
|
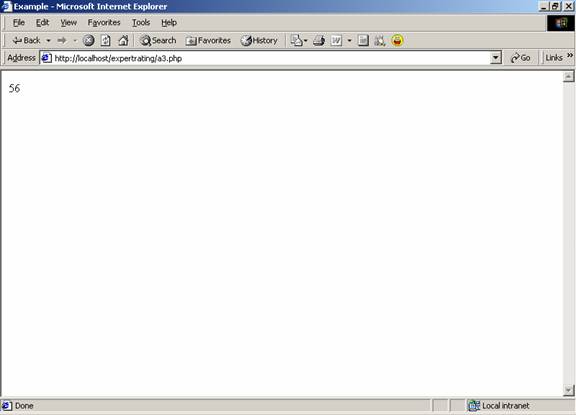
$txt=56; |
|
echo $txt; |
|
?> |
|
|
|
</body> |
|
</html> |
Output:
In order to concatenate two or more variables together while displaying the result on screen, use the dot (.) operator.
| Example |
|
<html> |
|
<head> |
|
<title>Example</title> |
|
</head> |
|
<body> |
|
|
|
<?php |
|
$abc="Welcome to expertrating!"; |
|
$xyz=56; |
|
echo $abc . " " . $xyz; |
|
?> |
|
|
|
</body> |
|
</html> |
Output:

Comments
In PHP, if a single line comment has to be made we use two backslashes //. If a double line or large comment block has to be made then it has to start with a /* and end with a */.
| Example |
|
<html> |
|
<body> |
|
|
|
<?php |
|
//This is a comment |
|
/* |
|
This is |
|
a comment |
|
block |
|
*/ |
|
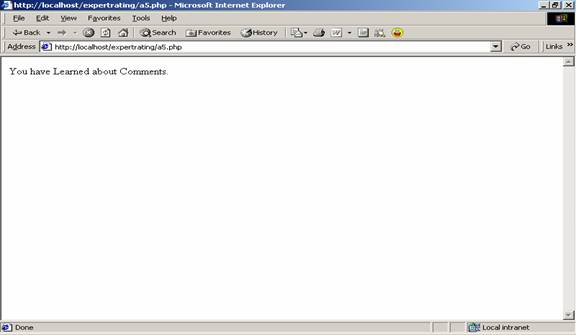
echo "You have Learned about Comments."; |
|
?> |
|
|
|
</body> |
|
</html> |
Output: